Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in South-Central Asia. It shares borders with Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north, and China to the northeast. The capital city is Kabul, which is also the largest city and a central hub of political, economic, and cultural activity.
Geographically, Afghanistan is characterized by its rugged terrain, dominated by the Hindu Kush mountain range, which stretches across the central part of the country. The landscape also includes vast deserts, fertile valleys, and significant river systems such as the Amu Darya and the Kabul River. This diverse topography has historically made Afghanistan a crossroads of various civilizations and a strategic location for trade routes like the Silk Road.
Afghanistan has a rich history that dates back thousands of years, with influences from various empires and cultures, including the Persian Empire, Alexander the Great, the Maurya Empire, the Islamic Caliphates, and the Mongol Empire. In the 19th and 20th centuries, Afghanistan became a focal point in the geopolitical struggle between major powers, known as the “Great Game,” and later faced invasions and internal conflicts.
In recent history, Afghanistan has experienced prolonged periods of conflict, including the Soviet invasion in 1979, the subsequent civil war, the rise and fall of the Taliban regime, and the U.S.-led invasion in 2001 following the September 11 attacks. The country has struggled with political instability, insurgency, and rebuilding efforts ever since.
Economically, Afghanistan is largely agrarian, with agriculture accounting for a significant portion of the GDP and employing the majority of the population. Key agricultural products include wheat, fruits, nuts, and opium poppies. The country is also rich in natural resources such as minerals, precious stones, and hydrocarbons, although these remain underdeveloped due to ongoing instability.
Culturally, Afghanistan is diverse, with numerous ethnic groups, including Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks, each with their own languages, traditions, and customs. The country has a rich heritage of poetry, music, and traditional crafts, despite the impact of decades of conflict. Persian (Dari) and Pashto are the official languages.
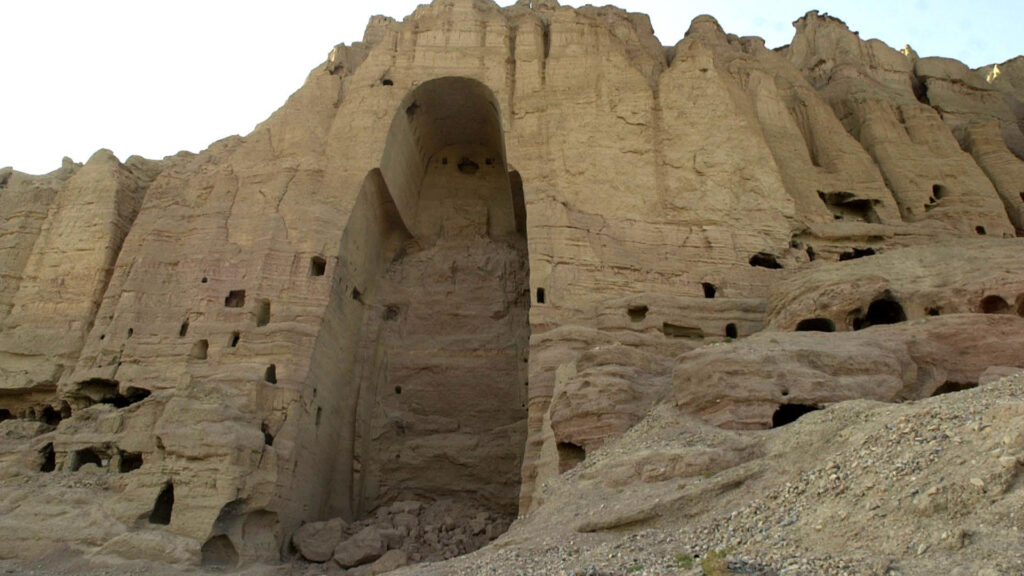
Despite its challenges, Afghanistan is known for the resilience and hospitality of its people, as well as its natural beauty, including the ancient city of Herat, the Bamiyan Buddhas, and the picturesque Panjshir Valley.
The future of Afghanistan remains uncertain as it continues to navigate complex political, security, and humanitarian issues. However, efforts by various domestic and international stakeholders aim to promote stability, development, and peace in the region.